Metrology Services Provider Levels, Calibrates, and Aligns Key Safety Testing Equipment
Large aircraft have a landing mass of up to several hundred tons. Regional aircraft have a landing mass of around 15 to 30 tons. The landing gear has to absorb all of the energy during landing. The individual landing gear components are subjected to enormous pressure loads. The safety of the entire aircraft depends on these parts reliably withstanding these loads. Aircraft manufacturers and suppliers therefore set up test rigs to test these load influences on the various components of an aircraft as well as the landing gear. The measured pressure loads from these tests provide aircraft manufacturers with crucial data for designing and producing safety-optimized components, as well as proving energy absorption for aviation certification.
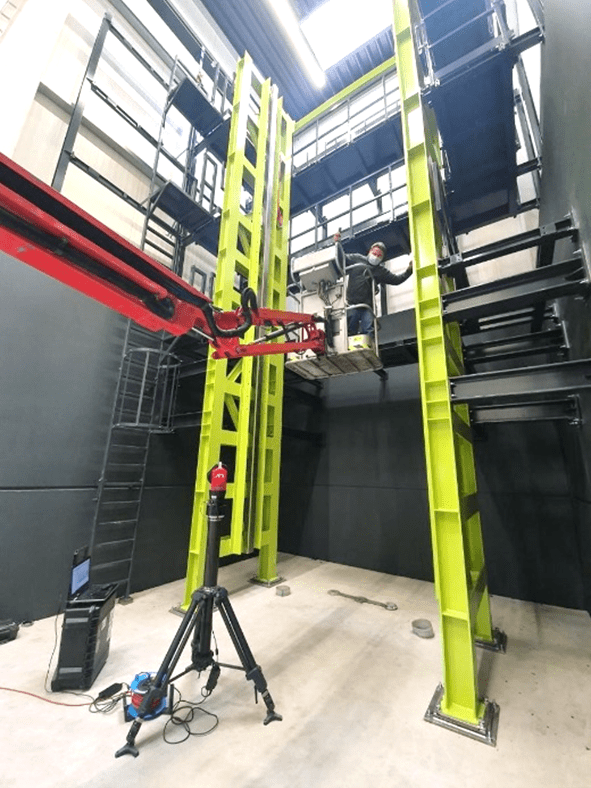
When HEGGEMANN AG needed to verify the installation of their new drop test rig for landing gears, they reached out to API Services to align, level, and calibrate all of the main features. Using the Radian Plus Laser Tracker, the Globally Local team at API Services was able to:
- Align the rails of the drop test rig vertically and horizontally
- Display real-time positioning during readjustment
- Document final position of the rails for as-left reporting
Test center for new aircraft and engines
Founded in 1962, HEGGEMANN AG is headquartered at Paderborn-Lippstadt Airport and is a supplier of complex metallic lightweight structures for international aerospace and automotive industries. All steps along the value chain are realized for their customers: from product development and series production to the production of ready-to-install structures and systems. (1) HEGGEMANN is currently building an aircraft test center for the development of new aircraft landing gears and novel low-noise and low-emission mobility concepts such as air cabs or transport drones.
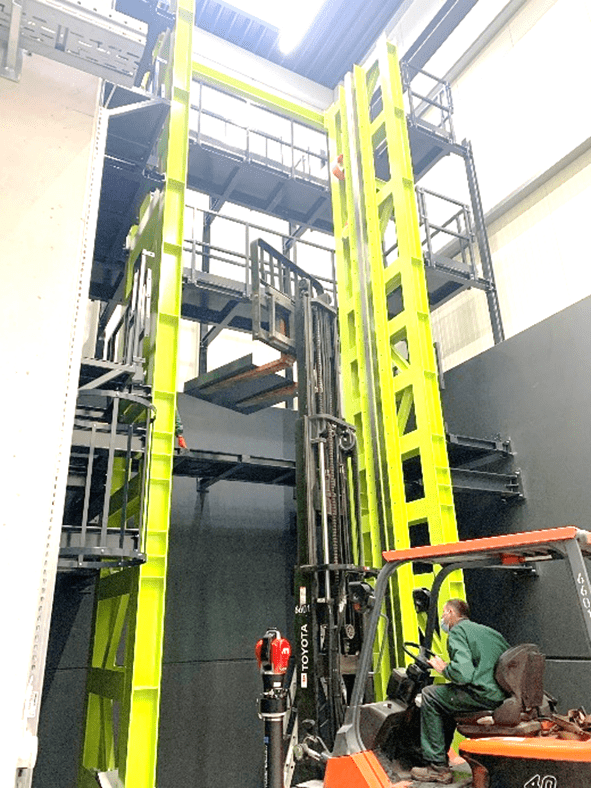
In the new test center, landing and decent pressure tests are simulated for various components of the aircraft. The components to be tested fall unbraked from heights of up to nine meters onto a measuring plate, where the forces of the fall are recorded and documented. Elements and landing gear systems up to the size of the nose gear of an Airbus A320 can be tested here. It is also possible to simulate landings of aircraft or drones for normal or emergency situations. (2)
Exact alignment of the rails of a drop test rig
The measurement results of the drop test rig depend on the exact alignment of the rig’s rails. This is the only way to simulate the forces acting on an aircraft landing gear during decent and landing. To ensure exact alignment from installation, HEGGEMANN AG decided to bring in some outside measurement expertise. They commissioned the Globally Local team of Real Metrologists at API Services to take measurements to ensure that the rails of the test rig were set up at the correct distance from each other and remained exactly perpendicular throughout the entire nine-meter height of the facility.
Level sensor of the API Radian is crucial
After discussing the project with HEGGEMANN AG and internally, the team at API Services developed a simple, efficient measurement plan that would align the rails quickly, accurately, and cost-effectively. API’s engineers arrived onsite and, using API’s Radian Plus Laser Tracker, were able to get right to work on the rails. Using Plus’s built-in level sensor, the team began recording reliable measurement data to begin precisely aligning the rails vertically and horizontally. And because the current measured values were displayed by the tracker’s software in real-time, HEGGEMANN AG was able to adjust the rails during measurement in a simple 3-step team effort:
- API’s service technicians operate the tracker and software, pointing out areas in need of adjustment.
- HEGGEMANN AG’s fitters adjust the rails optimally with the help of these measurements.
- The rail’s position is measured and recorded again to document its final condition.
Using this collaborative approach, API Services and HEGGEMANN AG were able to quickly align, level, and verify the position of the drop test rig’s rails and prepare the machine for operation. For leveling projects of all scales and levels of complexity, API’s Radian Laser Trackers are the tool of choice.
API Services’ qualified and highly motivated technicians offer a unique combination of OEM expertise on API’s state-of-the-art dimensional metrology equipment and real-world measurement experience on applications across every major industry. They meet all challenges and solve them by using the appropriate measurement technology and measurement software.
Photo source: See https://www.heggemann.com/de/branchen-produkte/service [21.07.2021] merged with API Service Man + Radian Laser Tracker
To learn more about our complete offering of contract metrology support and request yours today, click here: https://apimetrology.com/de/service/.
Or to learn more about Radian Laser Trackers and schedule a demo, click here: https://apimetrology.com/de/radian/.
You can read more about HEGGEMAN AG and their new test center at Paderborn Airport here:
2) https://www.nw.de/lokal/kreis_paderborn/bueren/22910578_Heggemann-baut-Flugzeug-Testzentrum-am-Airport-Paderborn.html – 02.12.2020 [21.07.2021]