Microservice, XD Laser Quickly Verify Tenova’s 3-Axis Machine Tool
MSP Precisely Verified High-precision Machine Tool with Significantly Reduced Time and Access Space
In order to ensure accuracy throughout the manufacturing process, measurements must be taken, regardless of how much space is available or how limited the time window is. Often, we associate these measurements with Laser Tracker inspections of complex parts with hidden features, but it can also be true for Machine Tool Calibration (MTC). Tenova needed to quickly verify the performance of one of their machine tools in Italy, in a space that did not allow much room for measurement equipment setup and operation. They called in the expert team at Microservice, who used API’s XD Laser to quickly and accurately verify the tool. Using XD, Microservice was able to:
- Perform accuracy checks for all axes in limited space
- Verify the tool in less than six hours
Tenova, a Techint Group company, is a worldwide partner for innovative, reliable and sustainable solutions in metals and mining. It has grown to a global presence as an industry leader in providing metals and mining engineering products and technologies, including those for smelting, hot formed, cold rolling, steel and aluminum work in addition to mining equipment, bulk material handling, and processing. The Tenova production team in Italy needed to test a high-precision 3-axis machine tool on a tight schedule and in an environment with significantly reduced access spaces, especially in the vertical axis, in order to verify the accuracy of a special grinding machine. And to perform this verification quickly in the available space, they reached out to the experienced professionals at Microservice.
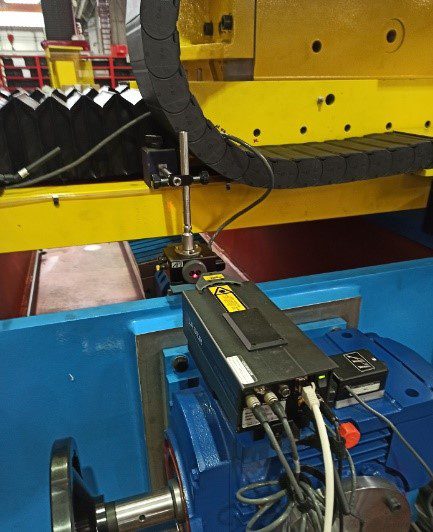
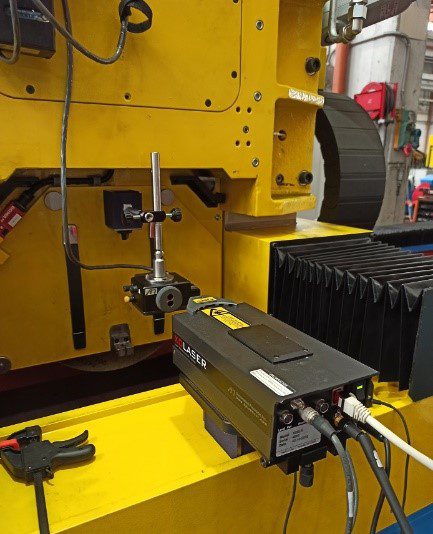
For nearly two decades, Microservice has been providing 3D Metrology Solutions from measurement to calibration to third-party equipment across Italy from their ISO 9001 and ACCREDIA certified laboratories. After evaluating Tenova’s machine and setup, the Microservice Team decided immediately for the accuracy and compactness of the API XD Laser Interferometer. With this 3D laser, Microservice was able to go onsite, setup the equipment, and perform the verification on all three axes required at the production site in less than 6 hours.
The fast results of the measurement and verification are a credit to all three parties involved. Tenova was able to rearrange subsidiary equipment in the inspection site to create a little more room for Microservice. The technicians from Microservice were able to adapt to the challenging conditions of space and expedited results to deliver accurate readings of all error parameters from the machine. Last, but not least, API’s XD Laser is the only system that can capture all six error parameters in a single setup. Its dynamic measuring range and mounting orientations allow for compressed inspection times, including equipment preparation and setup. The combination of Microservice’s experienced team and the speed, versatility, and accuracy of XD allow for exceptional execution time and quality of results.
“API’s XD Laser is the only system that can capture all six error parameters in a single setup. “
This was the first inspection job that Tenova performed for Microservice, and they were fully satisfied with the measurement results and service. Microservice was able to fully accomplish the mission, fulfilling it according the Tenova’s expected timeline and tolerances, from inspection execution to data report. Microservice’s quality performance has opened up future opportunities to work with Tenova to guarantee the quality of their metal and mining work.
The team at Microservice is on call for any challenges in the calibration and verification of machine tools by Tenova and other producers in Italy. Interested parties can contract their services via email: sales@micro3d.it or telephone: +39 011 9682 524.
API and Microservice have been working together for more than 15 years in the 3D measurement market. Microservice consults, sells, and supports the full range of API systems, including the Radian Laser Tracker Series, in addition to a wide range of related services. Every day, Microservice uses the API’s state-of-the-art laser-based dimensional metrology products and systems for third party measurement services, calibration of measuring machines, machine tools and industrial robots, and has developed specific skills to support customers in both selection and after-sales service at 360 degrees of the entire product range. API and Microservice will continue to answer every customers’ request, solve measurement tasks, and support current and future needs. Customers who have given trust to Microservice by purchasing API products can always rely on Microservice and their customer-oriented approach for which Microservice is known in the market.



Links from this article: